INSCRIPTION WRITTEN IN PERSIAN PAINTING METHOD OF “ NÈGARGARI ” Ahmadamiraghai Mehrdad

Key Words: Persian Nègargari, Thematic features, Structural features, (composition and movement) Functional features, Inscription written Researcher, Iranian cultural heritage, handicrafts and tourism organization
INTRODUCTION

such as (Mirmelas) and (Doushe), (karshourab) canyon or rock paintings of (Kouhdasht) and belonged to troglodyte Of The Iranian plateau. This art style that has been that its applications, themes and have been transformation in its historic development, as a visual art of Iran, still has a special place and is an example of an ancient culture and folk art of Iranian with narrative appearance and fantasy intrinsic.
1. Thematic feature
The subject of the painting is one of the characteristics of Persian Nègargari. Pre-historic patterns were usually Plants and geometric designs or human and animal images and motifs such as mountains, raging water, sun and moon. In later periods mythical creatures and animal motifs with special characters were formed that in most cases can be seen as base relief such as the ones in Persepolis etc., these mythical creatures had been shown as a combination of man and animals with four legs or wings. Before the beginning of the Islamic era, hunting scenes, trees and ivy designs, and human figures with short stature, round faces and narrow eyes which are Manichaean art features, had been formed in paintings and changes found the way to the Islamic era Nègargari. By the beginning of this period, a new approach was developed in Persian painting providing a context for the expression of artist’s talents in the illustration of books. Over time, Nègargari became more associated with mystical literature and epic and lyric poems with roots in ancient beliefs and histories like the heroic battles of the Shahnameh stories or stories such as Varghe and Golshah, Joseph and Zoleikha. These links were not only in the subject’s appearances, but also Painter had a common bond with the Creators of works in cases like the metaphor of Beloved stature to cypress, lips to flower bud, face to moon, bow to the brow and… However few topics with religious themes, as specific and separate works of book illustration, by several artists including Soltan Mohammed were emerged. “Meraj” which is a painting about the spiritual journey of the Prophet Muhammad at Night of ascension, royal and romantic scenes and portraits were some of the works that can be mentioned. Over time, based on the above themes and by taking advantage of the specific characteristics of each school, unique works were presented to Persian art history.
*Buy online Persian painting (negargari)*
2. Structural feature(composition and movement)

Composition principle is a set of rules and methods that are based on the artist’s vision and taste. In addition to the design and geometry, these rules can also take advantage of other
elements like color. In the other word, composition can be known as eye-catching and reasonable classification of the constituent elements of an art work. In the visual arts, variety of configurations had been used to convey the thoughts and feelings of the artist. Application of composition principles is related to art works subject to make it more able to transfer concepts. For example curve and circular composition helps induction movement in viewers saw, while triangle shapes transfer different feel.
Although the composition principle was used in past Persian art works like palaces, buildings and designs of pottery and steelworks but in early Islamic era, according to illustration prohibition, they had been used only in applied Tools such handicrafts. By passing time Nègargari had been growth and
developed especially by time that Nègargari found its way separated from book illustration and was manifested as an independent characteristic in years between 12 to 15 Centuries.
Study of these periods works show that composition structure of Persian Nègargari is based on circles and curves forms and spiral movements. Despite of diversity and distribution of
images and characters, center of vision and attention remains fixed. It is in full compliance with Muslims monotheistic belief in the unity that is the source and final outcome of all diversities and distributions.( Whatever he was, he returns again to it)
The results of these composition usages are creation of a systematic and meaningful structure by artist. The artist expresses abstractly the elements and structures by using rational composition that indicated his thoughts and feelings. In practice, it is assumed that the vision focus is more or less high, because characters have been painted from low to high level at painting surface. It seems that the characters and landscapes of the painting are seen from high altitudes and the horizon placed above painting space…. The last effect of this composition of forms to concept is circle of horizon that is used in most Persian miniature. In the other hand this method has the advantage of diverting realist. In fact, spirals patterns allow greater diversity and flexibility of images combinations in both forms and concepts. (Mousavi, 1982.P.72) In Heratschool, this composition has been applied in the best way with a variety in works of Master KamaluddinBehzad. In most of his works space segment, multiplicity and variety of objects and diversity of people with mobility is evident. In fact by using geometric methods of features composition and colors interaction, he had jointed different parts of image and achieved a general unification. Master Behzad used specific scale in his works with architecture concept but in most of the cases design of composition structure and its elements are based on circle. Putting elements in circle organization make feeling of an internal movement that became powerful by elements forms. (Pakbaz,2007, P.82). After him, the Nègargari ornamental dimension became more and according to complication of elements relationship and showing numerous events in art works, the structure had been much more variety, but the as the main structural characteristic of Nègargari, Composition had been still remained.[2] Movement factor is result of other factors of the work such as line, dot, level, rhythm, dimension… and cause the movement vision of viewers in different ways:
a. Line movement
b. Rhythmic movement( repetition of forms, colors, level,
b-1. Regularly (symmetric) b-2. Unregularly (non symmetric)
c. Induction movement
c-1. Direction each illustration in painting are followed ( like putting a triangle in right side of the picture with its point to the left side , inspire the viewer move to the left) c-2.Confrontation and conflict between two visual object that have been far from each other and cause a kind of tension in view Movement is shown in different way at Nègargari schools. In Baqdad school (Abbassi), less movement were used and human features seems to be fixed and artist had focused on other features of the paintings like trees and nature. After domination of Mongolian to Iran, during Ilkhanid period, chines methods of painting was effected on Persian Nègargari in Tabriz school (Saljuqi) dense areas, scene division to 3 original parts (foreground and background) twist of plants and trees as a combination factor to relate image’s parts together and usage of curves and spiral motion as a movement factor are main characteristics of this school art. Also Dramatic movements of human figures in motion picture and close cadres that focusing on the main issue must be included as featured of Persian Nègargari in this era. With the formation of the Shiraz School movement in paintings became simple and architectural issue and moving horizontally from right to left and vice versa were done.
In Timuridera the movement are shown in the most harmonic and balanced relationship between all parts and elements of art works in Harat school and taking advantage of the richness and brilliance of color with contrast color cause maximum dynamic visual. The high horizon line, which was introduced in Shiraz school and specific characteristics such as frame breakage can be seen in HaratSchool too. The final word is that connection between movements, composition and subject are one of the determination characteristics of this period paintings.
3. Functional feature
Before Islamic era, Persian painting was manifested in base relief, inscriptions and ornaments of potteries and metals vessels and tools and after that spent some time in isolation and stagnation but slowly found its place and developed as book illustration and layout in manuscripts or as a collection in form of book or scrapbook. Although its field work was not as extent and independent as the former, but this limited fields work allowed painters to creativity and use the creative power of imagination. At the beginning books that their scientific and technical aspects were superior to literary aspect, were illustrated like:
• Al-Adviyeh Al-Mofid (in medication science theme)
• Fe Almarefat Al-Khial Al-Hendeseh (in mechanical inventions theme)
• Aqaqir properties (in planets theme)
• Al-Qani (in music theme)
• Al-Beitareh (in veterinary theme)
• Al-Ashjar properties
• Jalinus medicine
Shortly after by more transplantation of Nègargari to history and literature books of these subjects like Vargheh and Golshah, Andarznameh, SamakAyar and Shahnameh had been illustrated . With the formation of the first art center in Tabriz, called “Rabe-Rashidi” or “Rashidieh” in the first half of the fourteenth century, the first book illustration workshop was formed. Several books included the biographies and historical ones were illustrated in groups. For instances KhavaranNameh, Javameh- Al-Tavarikh, Kelile O Demneh, Albaqiyeh and Manafeh-Al-heivan However, with the passage of time and from the middle of the sixteenth century, to the decreasing order of book illustration, Nègargari functions became more independently and in different formats such as: scrapbook (Album), large scale wall paintings, paintings of mirror boxes and etc.
4. Inscription written
There are calligraphic inscriptions on the painting that images are formed according to their texts. Although subject of texts in the painting are not considered here, but the way that they placement is very important. The inscription is on precisely calculated in points of number, size, location, and … and is a kind of composition and are created in coordinate with art work. As previously mentioned, composition of Persian Nègargari is formed on base of orbital and rotational motions, but the placement of the inscriptions in the art works usually the balance on whole work was interested by artists. However, in some cases inscription placement was the factor to focus on some particular point of painting. In general it can be said that the inscription on the painting are formed under the laws of geometry to create visual balance. In order to evaluate objectively the above issues, three art works will be studied as example.
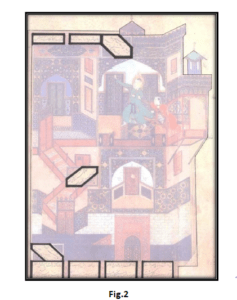
a. Escapes of Joseph from Zoleikha painting from Golestan book of Saadi, Herat school, by Master KamaluddinBehzad, 1475.
Inscriptions placement, proportions and their distance from each other, direction of inscription movement from bottom left to the top right of the picture and direction of above inscription to bottom, entirely cause focus on the human forms (Joseph, Zoleikha) on the painting. While looking to stairs in left side of the image, the inscription placement, general visual balance in addition to moving. (Figs.1, 2)
b. Painting from Shahnameh book of Ferdousi, Safavid School.
In this painting BaysunghurMirza among the group of courtiers while listening to the story of Rostam, is shown. In this work, the artist “Mirmosavar” due to the large number of human figures, created visual balance by drawing inscriptions on top of the painting. Also by placing of an inscription at the bottom, connection and balance between the upper and lower parts of the painting is created. (Figs.3, 4)
c. Ascension Prophet Muhammad Painting from Kamseh book of Nezami, Safavid School, Early periods of Sultan Muhammad.
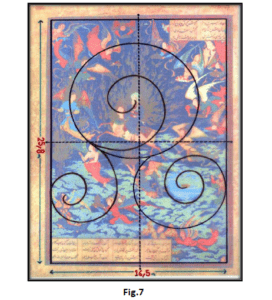
It has been created in 15th century and shows ascension of the Prophet Muhammadin among of Angeles’s group. The concept of the painting is totally religious and shows the excellence of the Prophet Muhammad as the perfect man towards the heaven. (Fig.5) This work composition is based on serpentine motion from bottom to above and leads to image of Prophet Muhammad. (Fig.6) Otherwise, the artist draws a circle in the above of the painting to equilibrium imbalance by two serpentine motions at bottom. (Fig.7) The main point is placement of inscriptions that include poems with related subject. Two inscriptions with 1/3 width of the painting are located on upper right side. At the bottom numbers of inscriptions are double with almost same proportion. If an imaginary line drawn from end of above inscription above to lower ones, they will quite intersect. Also by dividing the length of the painting, equal proportion of 1/12 will remain on both left and right sides of the painting. So it is quite appropriate to make a claim, writing inscriptions in Persian Nègargari are primarily based on geometrical rules and although composition feature is driven on the movement and rotation curves but Persian painters considered to visual balance. (Fig.8)
CONCLUSIONS
1. Content feature is one of the characteristics of Persian Nègargari that Carries the ancient and historical painting traditions that among years became more transplant to mysticism literature and epic and lyrical poems during Islamic eras.
2. Structural feature of Persian Nègargari by understanding the basics of intellectual space, that included composition and movement, plays connecting role between image and text. In fact ornaments as dominant elements, with their hidden mysteries, is the criterion measurement for understanding the aesthetics of this art style.
3. In Persian Nègargari, functional feature are manifested in different ways. Before Islamic era was express in base relief, inscription and ornaments of potteries and metals vessels and tools and in Islamic era slowly w developed as book illustration and layout in manuscripts or even as scrapbook.
4. Writing inscriptions in Persian Nègargari are primarily based on geometrical rules and although composition feature is driven on the movement and rotation curves but painters considered to visual balance.
NOTES
1. We are from Allah and will return to him
2. During years, 12 types of composition were used more by painters:
a. Centralized( most epic or religious composition in Renaissance and Neoclassical periods : Jacques-Louis David)
b. Circle (composition of funeral scene in “meeting of Rostam and Esfandiar “in Baisonghor’s Shahnameh or composition of Large stones of Stone Henge in Salzbry plain, UK)
c. Crossover(Most works of Piet Mondrian and Fritz Klarnd)
d. Triangle(Religious works of Leonardo da Vinci)
e. Skewed(Marcel Duchamp’s famous work called running down the stairs” and works of John Marin and Joseph Stella)
f. Symmetric(Iranian traditional works, Ancient Egypt and Indians of north and south America)
g. Spiral(Ascension of the Prophet by Sultan Mohammed, “Spiral pier “by Robert Smith)
h. Vertical(Ancient Egyptian works)
i. Maqami(Qahvekhane paintings, religious icons of Russia)
j. Raging (“Starry Night “by Vincent Van Gogh, “slippery squares” by Bridget Riley. “Wave “ by Hokusai)
k. Horizontal( works of Jack Bush and many of the works of Richard Diamond)
l. Diffused(Ancient Persian Nègargari, Qahvekhane paintings). (Hosseini,2003,P.64) (Album)scrapbook is a collection of various pieces of painting, drawing and
3.calligraphy in a book in certain manner. Page margins are usually illuminated in Tazhib and Tashier manner. Usually client and collectors names and a description are written as a prelude at the beginning and date of completion of the work will be included in at the end of the book.(Pakbaz,1999,P.9)
International Journal of Advanced Research in ISSN: 2278-6236
Management and Social Sciences Impact Factor: 6.284
Vol. 5 | No. 3 | March 2016 www.garph.co.uk IJARMSS | 334
REFERENCES
[1] Pakbaz .Rouyin. Encyclopedia of Art. (1999).Tehran.Culture and Art Publishing House. First Edition. 1033 pages
[2] The same source. Page 9.
[3] Pakbaz .Rouyin.Persian Painting from past to now.(2007). Tehran. Publication of gold and silver. Sixth Edition.228 pages
[4] Mousavi. Tabloid of Alexandre Papadopoulo. Part of the miniature. Islam and Islamic art. Art Journal. No. 2. (1982). Tehran. Ministry of Culture and Islamic Guidance. 460 pages
[5] Hosseini, Mehdi. The concept of space in folk paintings. Art Journal. No. 55. (2003). Tehran. Ministry of Culture and Islamic Guidance. 242 pages